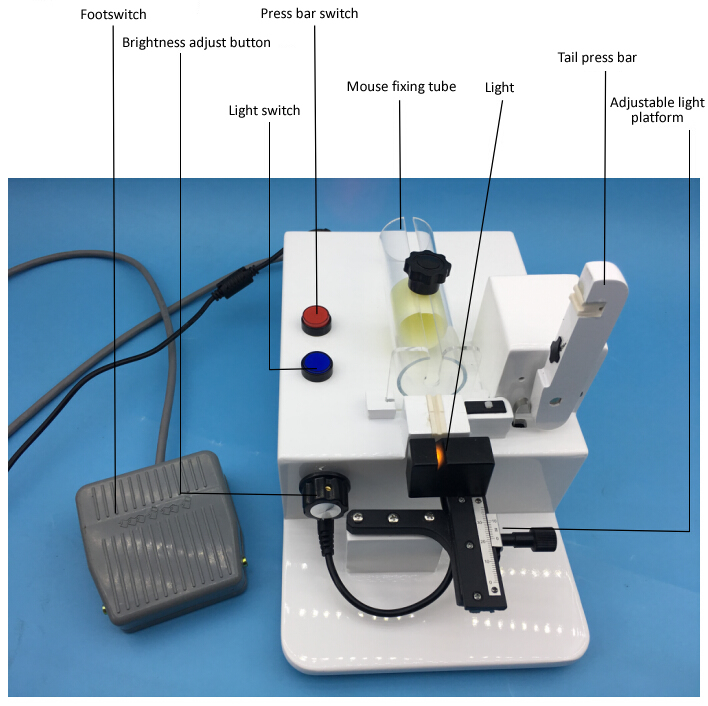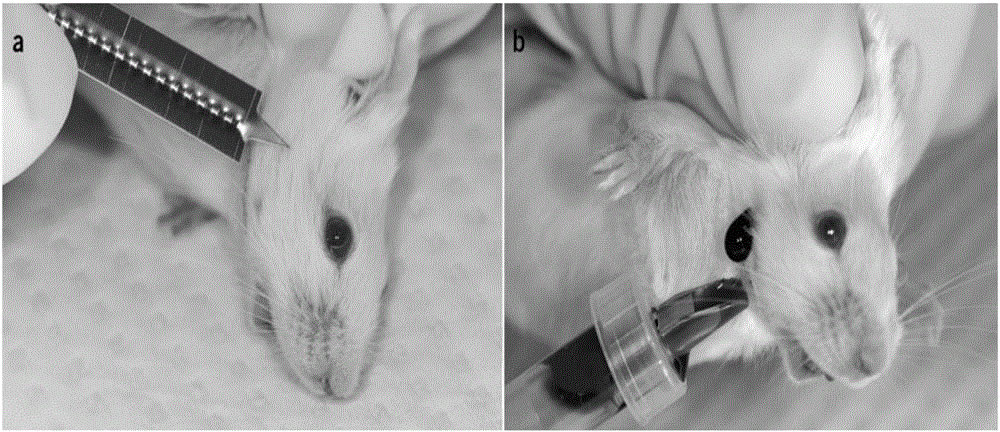
Mice are the most commonly used animal models in medical research and clinical trials because their genetic sequences are highly similar to humans. Especially in physiological, pharmacological, and pharmacokinetic studies, their blood is often collected for cytological experiments. Physiological and biochemical analysis to collect blood samples from mice is an essential ability for successful experiments.
There are many blood sampling methods from mice, but each of them has its advantages and disadvantages.
Cardiac puncture is complex and can lead the mice to death.
Decollation blood collection can only be operated one time because the hair and the tissue fluid often contaminate the blood sample.
Anesthesia is a must-have for the posterior orbital artery, femoral artery, vein, carotid arteries, abdominal aorta, and other puncture blood collection methods, making the operation complicated. Wounds of those methods are significant, and counts of blood collection are limited.
The decollation method for blood collection is time-consuming and less blood volume.
Studies show that routine experimental operations, especially blood sampling operations, will cause stress reactions in experimental animals and change corresponding physiological and biochemical indicators such as corticotropin and cortisol in rats. So try to minimize the stimulation of experimental animals during the operations is important.
Mice submandibular blood collection is the fastest, simplest, and humanized method so far, which minimizes the harm to mice during blood sampling of experimental mice.
Materials and collecting methods
- Experimental animals
20 male SPF-grade ICR mice, weighing 18-22 g - Experimental equipment
20 μL microcapillary pipette, conventional 1.5 mL sterilized centrifuge tube, alcohol wipes, sterilized cotton ball, heparin, etc. - Methods
The steps of the submandibular vein blood collection method are as follows:- Determine the blood collection point: Anesthetize the mouse with 5% chloral hydrate solution. The dosage is 0.1ml/10g of mice’s weight.
- Overall, look at the mouse head; there are 2 hairless sites on the mandible’s left and right spots.
- Perform anatomy of the maxillofacial blood vessels; the external jugular vein was divided into two branches at the superficial part of the maxillofacial region: one ascending to the eye. Another descending along the lower edge of the masseter muscle, through the mandibular spot, where the blood vessel location is superficial, and the projection position is clear and easy to locate, is the experimental blood collection point.
- Use a 20 μL micro-capillary pipette instead of a metal needle; autoclave it before use. Put one end of the micro-capillary pipette into the collecting location, keep another end 6cm.
- Fix the mouse with the right hand, pull its tail backward, clamp the ears with the thumb and index finger of the left hand, and press its back and tail with palm and other fingers, make sure no swing of mouse’s head.
- Submandibular blood collection: fix the mouse with your left hand, invert it for a few seconds to fill blood vessels in the head with enough blood flow, and find the mandibular spots in the head and rub the blood collection position with an alcohol wipe, plunge a micro-capillary pipette vertically into the position, and the blood will flow out. After completion of the collection, compress the wound with a sterile cotton ball immediately.
- Collect the blood into a 1.5mL sterilized centrifuge tube and number it for future use. Observe the mouse for 10 days after the blood sampling, monitor their diet, behavioral activity, infection, and death.
- Results
Submandibular blood collection of 20 mice and blood collection volume of each mouse is 0.5-0.7mL. The blood has almost no hemolysis in the collected blood, and the serum is clear and transparent after centrifugation.
During the blood collection, one mouse died after successful sampling. No disability or death happened for the remaining mice. And there is no abnormal behavior, infection, or death after 10 days of the collection.
Blood collection data:
| Number of samples | Body mass/g | Blood volume/mL | Sampling/s |
| 20 | 22.22±1.16 | 0.54±0.08 | 43.6±8.32 |
The submandibular vein blood collection method is repeatable, and damage to mice is minor, easy to operate, and the mice can recover quickly.
However, there are still several shortcomings that need to be improved:
- First, the position of the blood collection is not easy to locate.
- Second, the general method uses venous blood collection needles or syringe needles to pierce the skin, then let the blood drip in the collecting tube. It may contaminate the blood due to the blood is easy to contact the skin and hair.
- After comparing different blood collection methods, submandibular vein blood collection is the best choice because it is repeatable. Cardiac puncture and eye extraction methods can not apply repeatedly, but they have a high volume of collecting blood.
- The improvement is we use a micro-capillary pipet which is usually used in the method of orbital venous plexus collection, to avoid contamination of the blood sample method of the submandibular vein. Even beginners can find the position of the blood collecting and pipet the blood efficiently.
Advantages of the submandibular vein method after improvement
- The required equipment for blood collection is easy to access and universal.
- The blood collection point is clear and easy to identify, especially for beginners.
- The damage is slight, and the time consuming for blood collection is short. Experienced operators can master the sampling point’s location and suitable depth of blood collection to minimize the wound.
- The average sampling volume is up to 0.5mL for a single mouse.
- The micro-capillary pipet is for collecting blood, avoiding skin, hair, tissue fluid contamination, and lower hemolysis.
- The blood sampling is repeatable, efficient, and easy.
- For the mice, it is a humanized method.
Key points during blood collection
- Mouse head fixation is vital to implement sampling successfully. Make the skin tight by using one hand to grasp the mouse neck’s skin, and then it will be easier to pierce and fix the blood collection pipet. After the head fixation, invert the mouse for 10 seconds so the blood can flow near to the collecting point.
- Do not hold the neck skin too tight, which may cause mouse death because of suffocation.
- Find the needlepoint and place the needle or pipette vertically; insert the needle 1~3mm inside the skin. Stop the inserting if the pipet touches the jaw bone.
- Invert the mouse during the blood collection process can increase the blood collection volume and cause its death due to excessive blood loss.
- Follow the principle of sterility.
- Feed the mouse with water only(no food) 12 to 24 hours before the process of blood collection, or intragastrically with 1mL of water within 0.5 to 1 hour before blood collection, can increase blood volume and lower death rate.